Epsilon for ANOVA from F and Sum of Squares
Description
This function displays epsilon squared from ANOVA analyses and its non-central confidence interval based on the F distribution. This formula works for one way and multi way designs with careful focus on the sum of squares total calculation.
The formula for $\epsilon^2$ is: $$\frac{df_{model} \times (MS_{model} - MS_{error})} {SS_{total}}$$
The formula for F is: $$\frac{MS_{model}}{MS_{error}}$$
R Function
epsilon.full.SS(dfm, dfe, msm, mse, sst, a = 0.05)
Arguments
- dfm = degrees of freedom for the model/IV/between
- dfe = degrees of freedom for the error/residual/within
- msm = mean square for the model/IV/between
- mse = mean square for the error/residual/within
- sst = sum of squares total
- a = significance level
Example
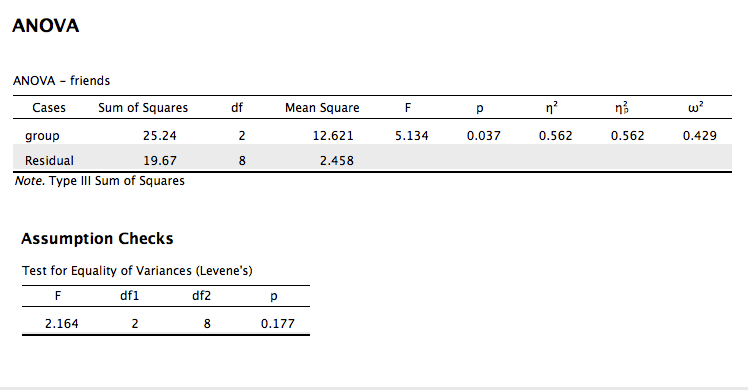
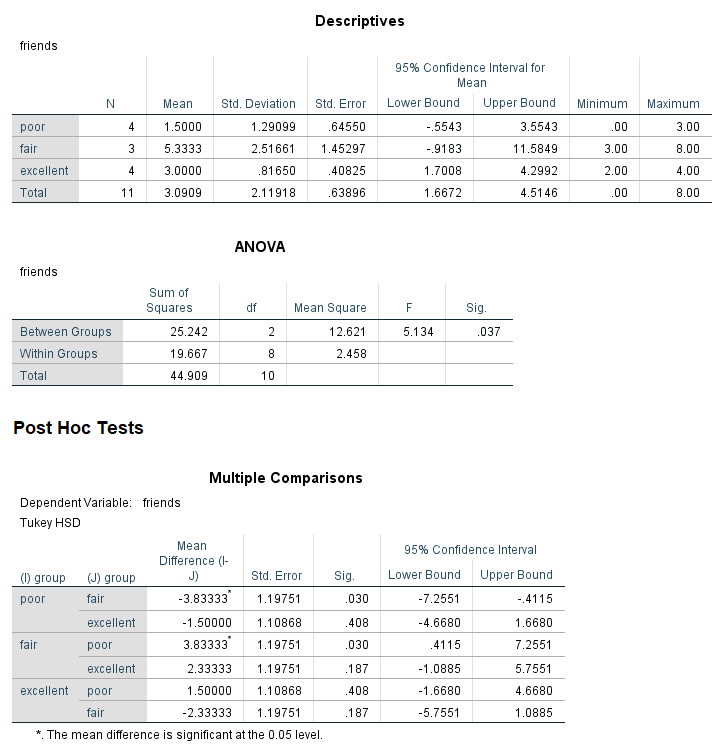
A health psychologist recorded the number of close inter-personal attachments of 45-year-olds who were in excellent, fair, or poor health. People in the Excellent Health group had 4, 3, 2, and 3 close attachments; people in the Fair Health group had 3, 5, and 8 close attachments; and people in the Poor Health group had 3, 1, 0, and 2 close attachments. The data are available on GitHub. Example output from JASP, SPSS, and SAS are shown below.
JASP
SPSS
SAS
Function in R:
epsilon.full.SS(dfm = 2, dfe = 8, msm = 12.621, mse = 2.458, sst = 44.909, a)
MOTE
Screenshot

Effect Size:
$\epsilon\^2$ = .45, 95% CI [.00, .77]
Interpretation:
Your confidence interval does include zero, and therefore, you might conclude that this effect is similar to zero.
Summary Statistics:
F(2, 8) = 5.13, p = .037
Test Statistic:
Not applicable.
Interpretation:
Your p-value is less than the alpha value, and therefore, this test would be considered statistically significant.
