r and Coefficient of Determination (R2) from d
Description
Calculates r from d and then translates r to $r^{2}$ to calculate the non-central confidence interval for $r^{2}$ using the F distribution.
The formula for r is: $$r = \frac{d} {\sqrt{d^2 + \frac{(n_1 + n_2)^2}{(n_1 \times n_2)}}}$$
The formula for t is: $$t = \frac{r} {\sqrt{ \frac{1-r^2} {(N - 2)}}}$$
R Function
d.to.r(d, n1, n2, sd2, a = 0.05)
Arguments
- d = effect size statistic
- n1 = sample size group one
- n2 = sample size group two
- a = significance level
Example
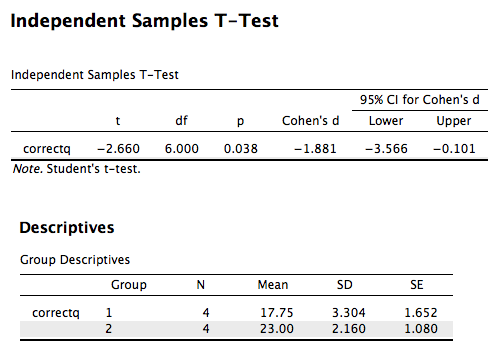
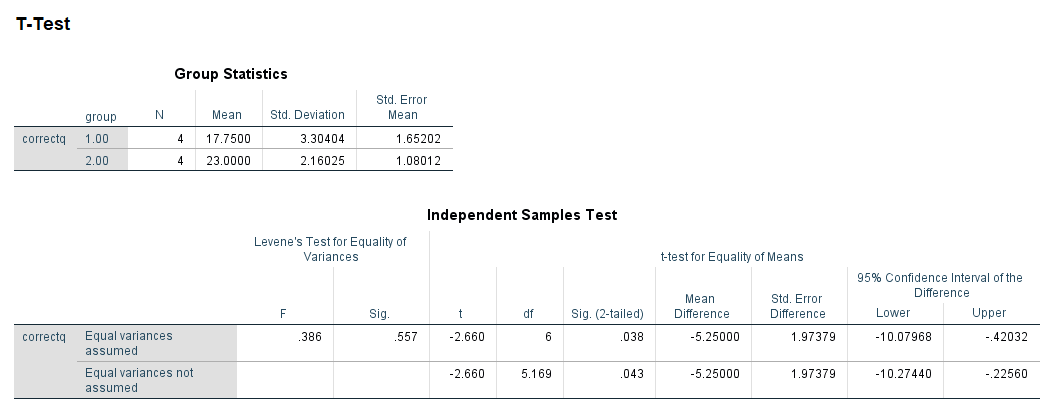
In a study to test the effects of science fiction movies on people’s belief in the supernatural, seven people completed a measure of belief in the supernatural before and after watching a popular science fiction movie. Higher scores indicated high levels of belief. The mean measure of belief on the pretest was 5.571, while the posttest average score was lower, 4.429. The data are available on GitHub. Example output from JASP, SPSS, and SAS are shown below.
JASP
SPSS
SAS
Function in R:
d.to.r(d = 1.881, n1 = 4, n2 = 4, a = 0.05)
MOTE
Screenshot

Effect Size:
r = .69, 95% CI [.00, .92]
Interpretation:
Your confidence interval does include zero, and therefore, you might conclude that this effect size is similar to zero.
Effect Size:
$R^{2}$ = .47, 95% CI [.00, .84]
Interpretation:
Your confidence interval does include zero, and therefore, you might conclude that this effect size is similar to zero.
Test Statistic:
t(6) = 2.30, p = .061
Interpretation:
Your p-value is greater than the alpha value, and therefore, this test would be considered not statistically significant.
